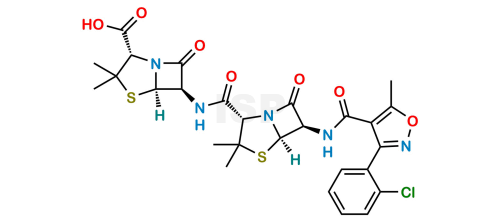
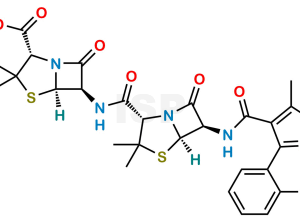
Cloxacillin EP Impurity E
| Mol.F. | |
|---|---|
| Mol.Wt. | |
| Inv. Status |
Disclaimer
The product information provided on this website by ISPStandards is based on the best available understanding at the time of publication. Customers are responsible for verifying the accuracy of this information before making a purchase. ISPStandards may update product details as new information or specifications become available, without prior notice.
- Product Overview
- Description
- Technical Data
Description
Chemical Name: (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[[(2S,5R,6R)-6-[[[3-(2-Chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-yl]carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid
Synonym: 6-APA Cloxacillin Amide
Shipping Temperature:
Ambient
HSN Code:
38229010
Country of Origin: India
Smiles: O=C([C@@H](C(C)(C)S[C@]1([H])[C@@H]2NC([C@@H](C(C)(C)S[C@]3([H])[C@@H]4NC(C5=C(C)ON=C5C6=CC=CC=C6Cl)=O)N3C4=O)=O)N1C2=O)O
Additional Information
Cloxacillin EP Impurity E is chemically (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[[(2S,5R,6R)-6-[[[3-(2-Chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl]carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-yl]carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid.
It is also known as 6-APA Cloxacillin Amide.
Cloxacillin EP Impurity E is supplied with detailed characterization data compliant with regulatory guideline. Cloxacillin EP Impurity E can be used for the analytical method development, method validation (AMV), Quality Controlled (QC) application for Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) or during commercial production of Cloxacillin.
The product can be used as reference standards and further traceability against pharmacopeial standards (USP or EP) can be provided based on feasibility. ISP Standards products are for analytical purpose only and not for human use.
Application of quality by design concept to develop a dual gradient elution stability-indicating method for cloxacillin forced degradation studies using combined mixture-process variable models